"Archeology is anthropology or nothing" used to say the famous American archaeologists Gordon Willey and Philip Phillips in 1958, thus theorizing a course of research in archeology that, although understood by many, was practiced by very few. The two set the objectives of archaeological research as studying and solving human, cultural and social problems, and anthropology became a tool of obtaining that information and knowledge.
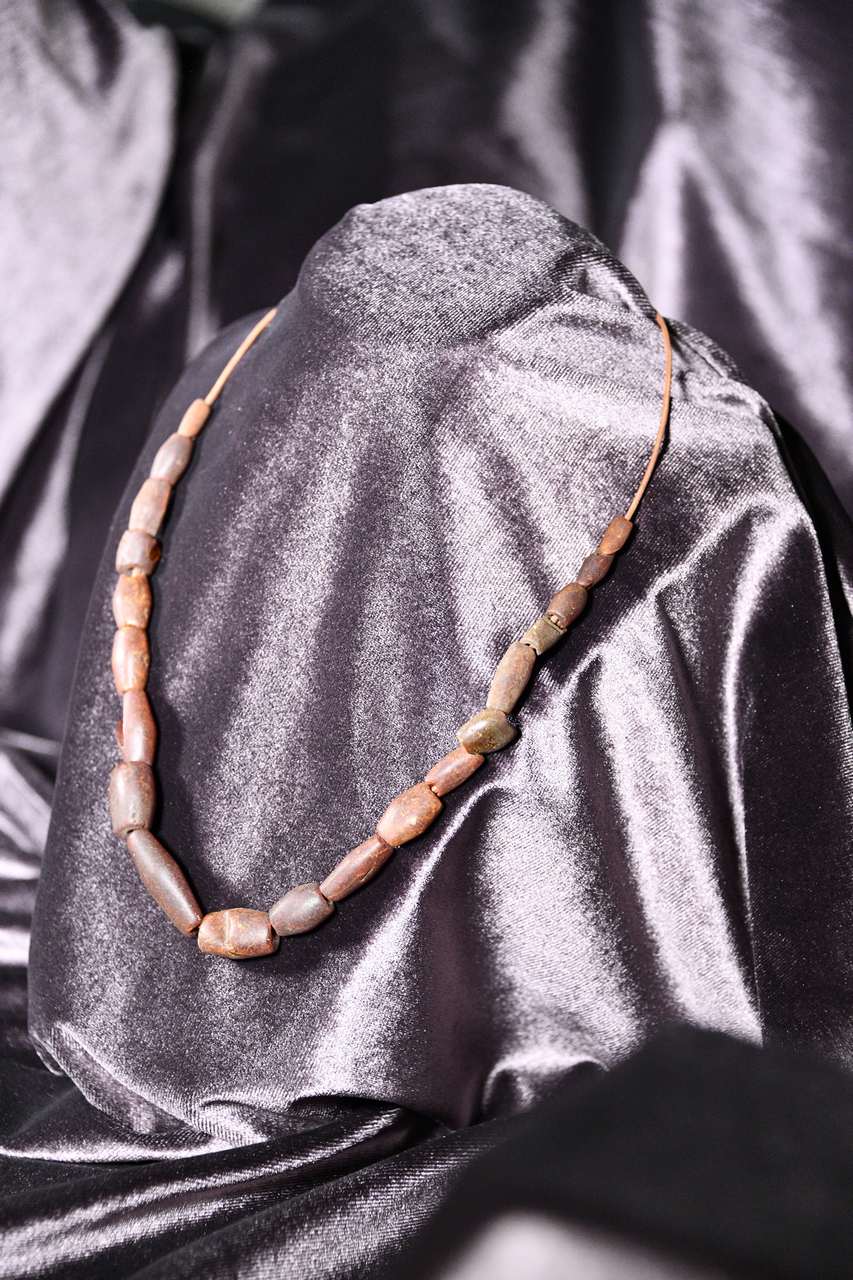
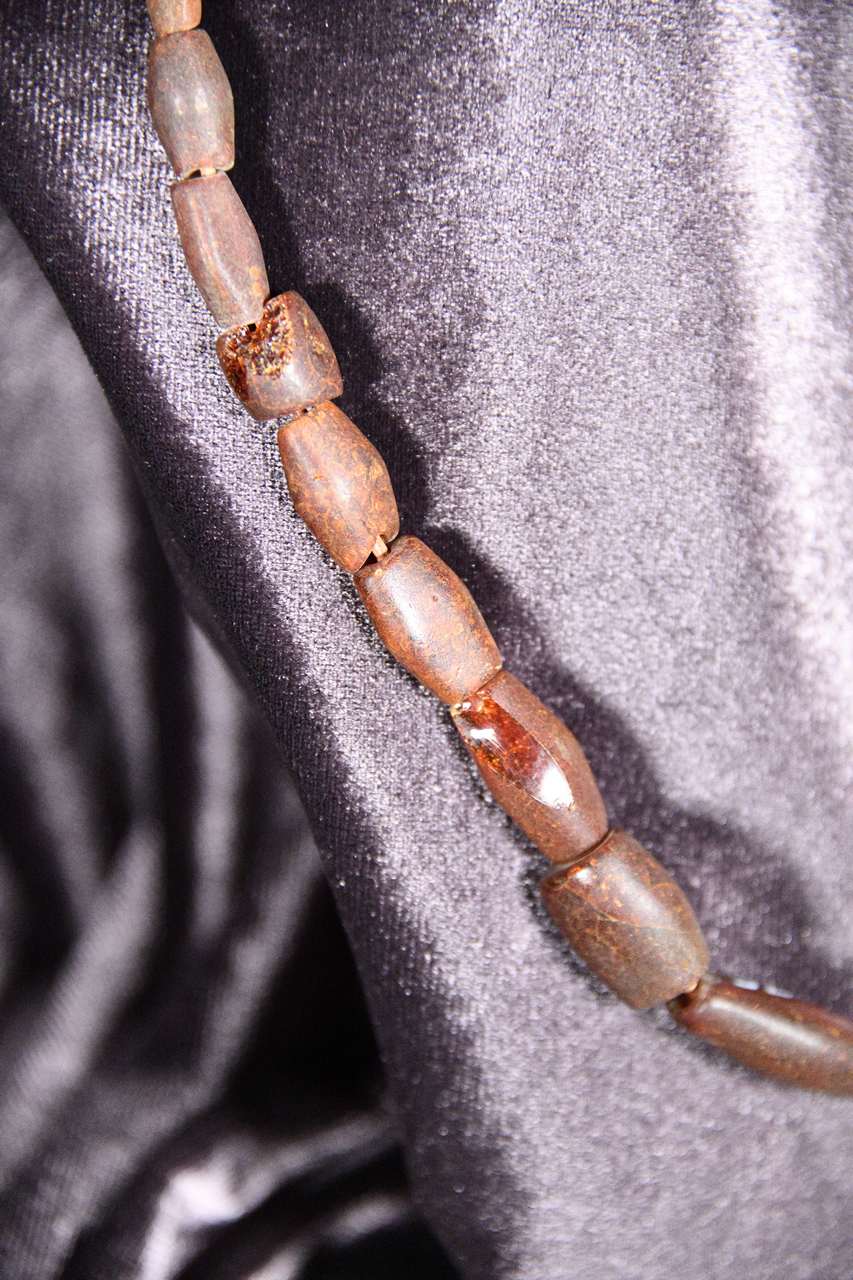
In complex archaeological research, absolutely all recovered fragments are important, whether they represent the results of human activity - artifacts (ceramics, clothing and ornaments, tools made of different materials, weapons, etc.) or osteological material itself. Their interdisciplinary research provides additional data to help complete the daily picture and work of the past.
This exhibition, which brings together archeological artifacts of particular importance, through the sum of their knowledge and osteological materials of special significance, represents a "bridge" through which today's archaeologists and anthropologists "speak" with our predecessors. By analyzing them, we can now know what physical activity they have had, why diseases have suffered and how they have tried to treat some, what were the conditions they lived and what they fed, what rituals they practiced and what has remained behind them. Their histories are fascinating, and their secrets are revealed.
The narrative behind this exhibition was born in the context of extensive research on the human skeleton in recent years, which has often become an avoided subject in different societies. Viewed and accepted differently, often with negative connotations, the skeleton represents for researchers a valuable source of information. Treated and interpreted with great care for all the details, it helps to reconstitute scenes and aspects of the lives of long gone human communities.
The exhibition presents, in chronological order, funerary complexes from the Paleolithic to the Middle Ages, associated with the inventory of graves, sometimes richer, sometimes more austere, defining and representative for the periods concerned. The most spectacular cases recorded by archaeological and anthropological science are highlighted: skulls with intentional ritual deformations, skulls with traces of "surgical" interventions, bones with traces of pathologies or traumas, are the messengers through which we are now closer to the life, activity, spirituality and beliefs of the past.
The concern for the body manifested more or less by man, has left legible traces in our bone matrix since old times. Whether it took the form of aesthetic care, whether it was in the curative field, all the actions to which the skeleton was subjected left its mark on the surface or in the structure of the bones.
Communicating with the people of the past becomes even more interesting the more unusual are the stories that are hidden in their bones.
The exhibition project „ArheOS: when anthropologists and archaeologists make bones to speak" is the achievement of an extraordinary team, it is the cumulative effort of some major and important research institutions: National Museum of History of Moldova and the Anthropological Research Center „Olga Necrasov", the Romanian Academy - Iaşi Branch, Romania.
Curators: drd. Mariana Vasilache-Curoșu (Chișinău) and dr. Angela Simalcsik (Iași).