>>>

One of the great technical achievements that revolutionized the idea of time and space, opening a new era in the history of communication, is telegraphy. It is based on the transmission of electrical signals through a cable over long distances, allowing people to communicate instantly. The telegraph spread very quickly and a network of wires stretched around the world.
In 1837, the American painter and physicist Samuel Morse invented the first electromagnetic device for telegraphy, patented in 1840. To send messages by wire, Morse developed in 1838 a simple code of dots and dashes, which represented the letters of the alphabet, known as "Morse code ".
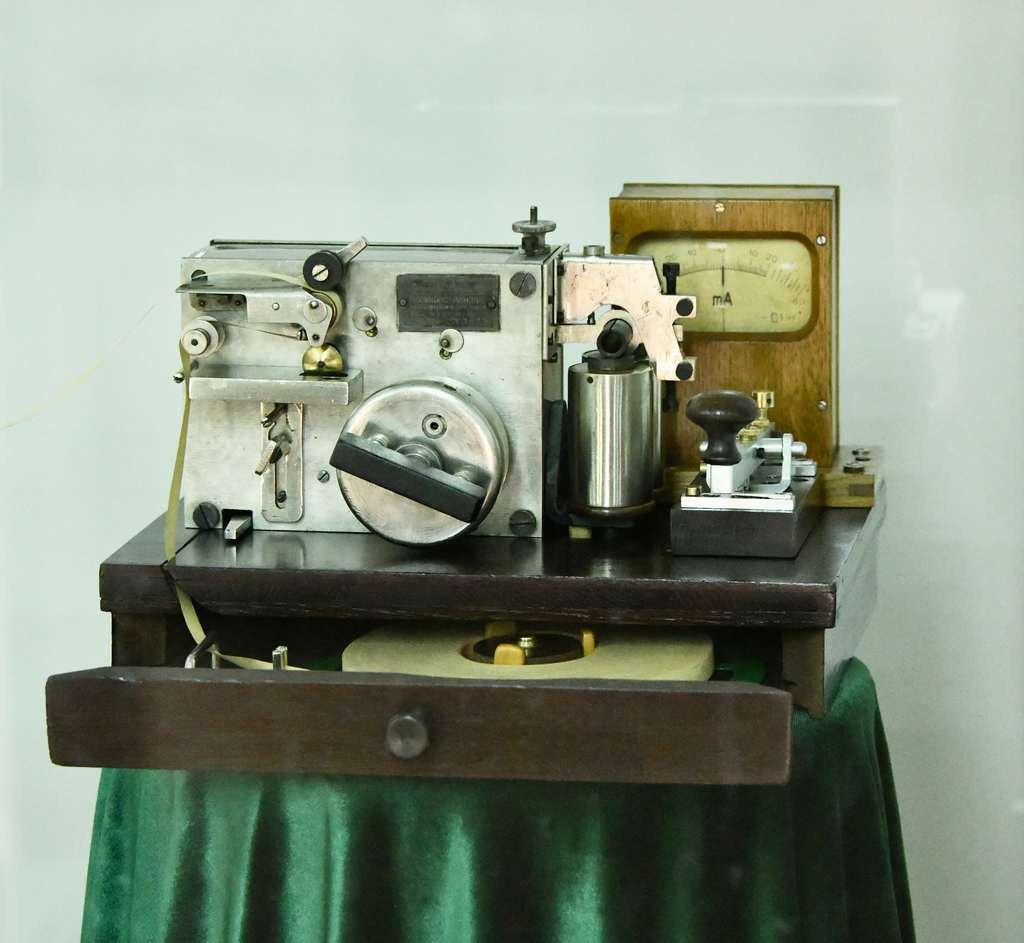
Both Morse code and the telegraph machine were improved over time, with the telegraph becoming the most widespread system of communication and information transmission for more than a century, until the advent of the Internet. The telegraph system consisted of a series of stations repeaters along the transmission line route. Each station had an operator who received and transmitted messages by telegraph. The Morse machine transmitted about 25 words per minute, which were recorded in code on a paper tape. The operator in charge of transmitting the message would decode it and write it on paper using a special typewriter.
In Bessarabia, the telegraph entered in 1860: on April 8, the Bender telegraph station began its activity, and on April 24, the one in Chisinau, following the construction of the first Odesa-Chisinau-Leova telegraph line. Currently, telegraph services have been discontinued. The only ones who still use coded communication are radio amateurs.
The Morse telegraph machine shown comes from the Osinoostrovsky electrotechnical plant, Soviet Union, and dates back to 1934. The exhibit was restored by Mihail Culașco.