>>>

Porcelain is a material that has sparked great interest throughout history, and its production has been a true challenge. Also known as "white gold," porcelain is a white, translucent ceramic material obtained by firing a paste of kaolin, quartz, and feldspar, along with other additives, at high temperatures. It was first discovered and used in China. The first Chinese porcelain objects arrived in Europe in the 13th century, but a broader spread of Chinese porcelain on the European continent is recorded in the 17th century. The technology for producing porcelain was kept a secret by the Chinese for a very long time.
The first hard-paste porcelain manufactory in Europe, located in the city of Meissen, was established in 1710 due to discoveries in porcelain production made by Saxon mathematician and physicist Ehrenfried Walter von Tschirnhaus (1661-1708), which were put into practice by the royal court alchemist Johann Friedrich Böttger (1682-1718). He invented the glaze and achieved the complete fusion of the shard and the glaze. The Meissen factory, still operational today, has created and continues to create a vast range of porcelain products. Crafted by the finest artists, sculptors, and engravers, who use unique hand-painted colors and exclusive designs, Meissen products are of exceptional quality and elegance, enjoying worldwide fame.
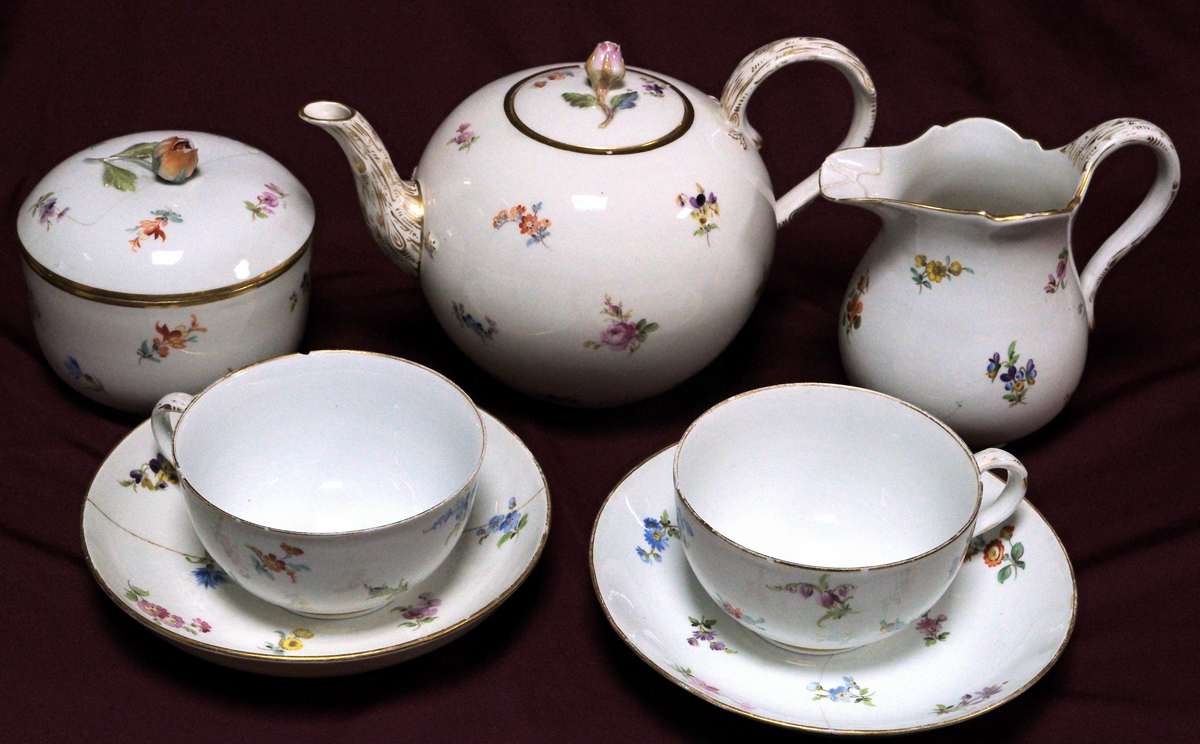
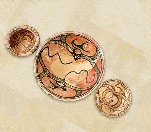
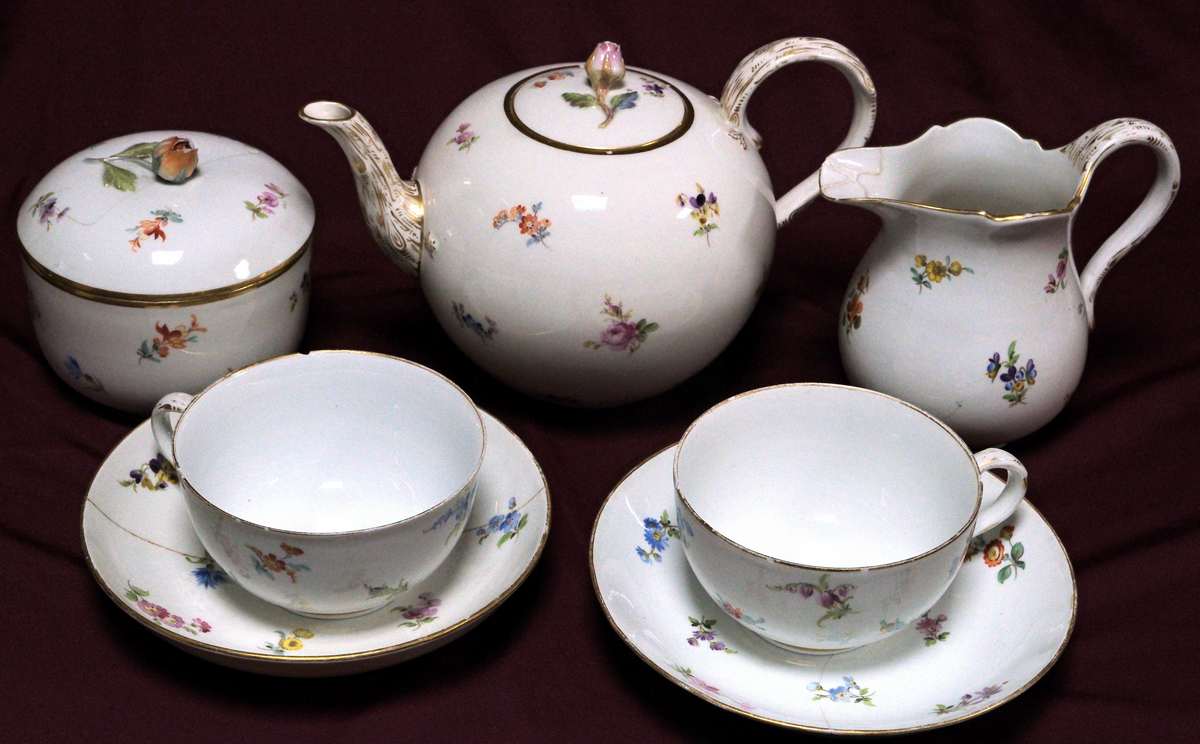
The tea set, partially consisting of seven pieces (teapot, milk jug, sugar bowl, and two cups with saucers), displayed in this showcase, is a product of the famous Meissen factory in the Kingdom of Saxony, Germany. It was crafted in the first half of the 19th century from high-quality porcelain. The exhibit became part of the collection of the National Museum of History of Moldova through a transfer from the "G. Cotovschi" Memorial House in Hâncești, which was closed in 1989-1990.
 The decoration of these pieces is remarkable, featuring hand-painted "German flowers," one of the well-known styles of floral and plant decoration practiced by Meissen craftsmen since the 18th century. They were influenced by Chinese porcelain, which was often adorned with images of flowers and fruits. A distinctive feature of this decorative style was the "scattered flowers" arrangement, where floral elements were placed as individual blossoms or bouquets across the surface of porcelain objects.
The decoration of these pieces is remarkable, featuring hand-painted "German flowers," one of the well-known styles of floral and plant decoration practiced by Meissen craftsmen since the 18th century. They were influenced by Chinese porcelain, which was often adorned with images of flowers and fruits. A distinctive feature of this decorative style was the "scattered flowers" arrangement, where floral elements were placed as individual blossoms or bouquets across the surface of porcelain objects.
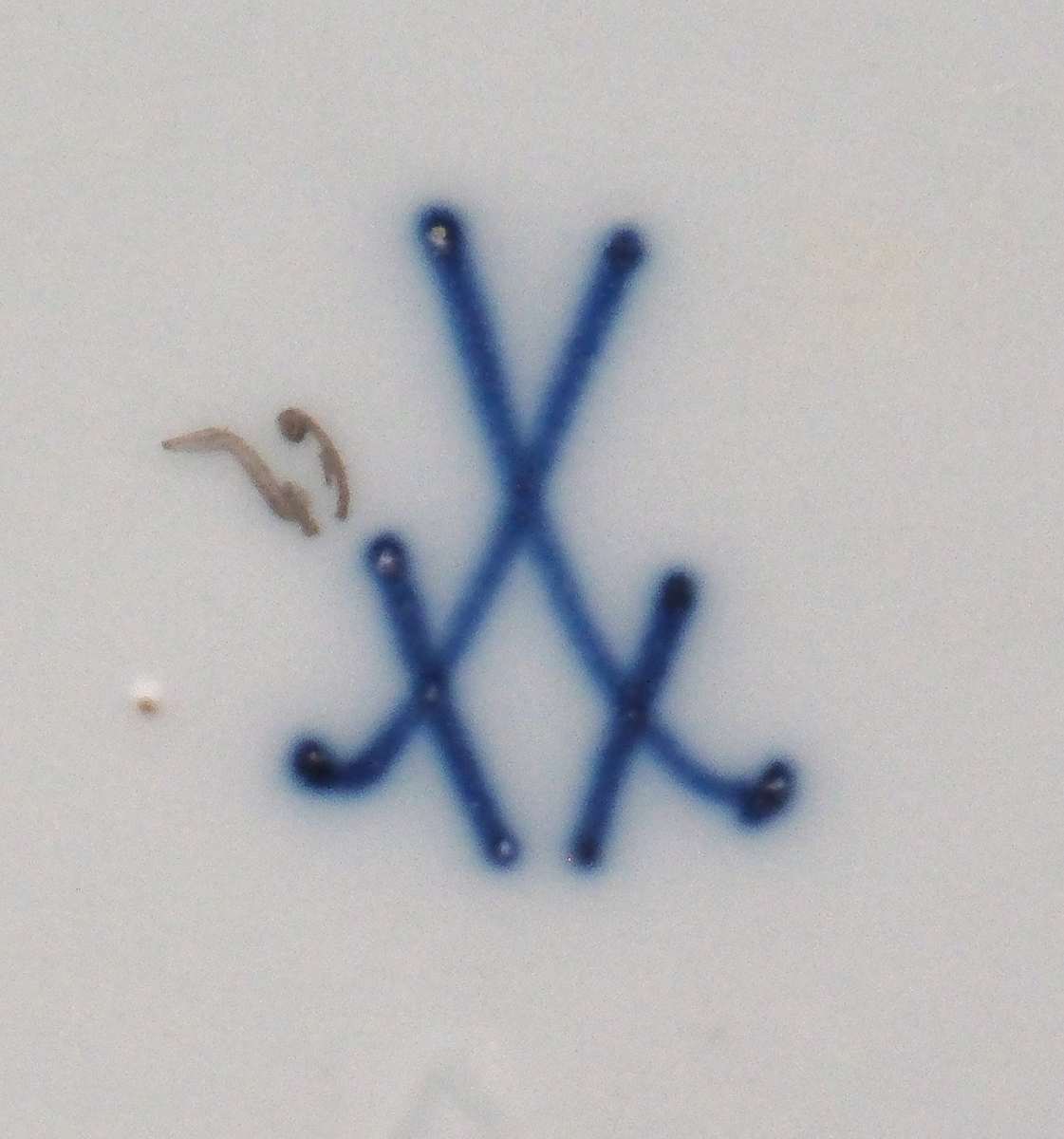
The marking on the underside of the pieces consists of two crossed swords, elements borrowed from the coat of arms of the Kingdom of Saxony, applied by hand with cobalt paint under the glaze. With slight variations in the representation of the swords, this mark has been used since 1722 and continues to the present day. The mark on this tea set is characterized by prominent dots on the crossed swords, a feature used at the Meissen factory between 1815 and 1860.
The polychrome floral painting, gilding, and the application of a rosebud on the lids of the teapot and sugar bowl lend a sublime delicacy to these pieces, making them rare and exquisite.











 31 August 1989 St., 121 A, MD 2012, Chisinau, Republic of Moldova
31 August 1989 St., 121 A, MD 2012, Chisinau, Republic of Moldova




 The decoration of these pieces is remarkable, featuring hand-painted "German flowers," one of the well-known styles of floral and plant decoration practiced by Meissen craftsmen since the 18th century. They were influenced by Chinese porcelain, which was often adorned with images of flowers and fruits. A distinctive feature of this decorative style was the "scattered flowers" arrangement, where floral elements were placed as individual blossoms or bouquets across the surface of porcelain objects.
The decoration of these pieces is remarkable, featuring hand-painted "German flowers," one of the well-known styles of floral and plant decoration practiced by Meissen craftsmen since the 18th century. They were influenced by Chinese porcelain, which was often adorned with images of flowers and fruits. A distinctive feature of this decorative style was the "scattered flowers" arrangement, where floral elements were placed as individual blossoms or bouquets across the surface of porcelain objects.