#Exhibit of the Month #Exhibit of the Month
September 2023
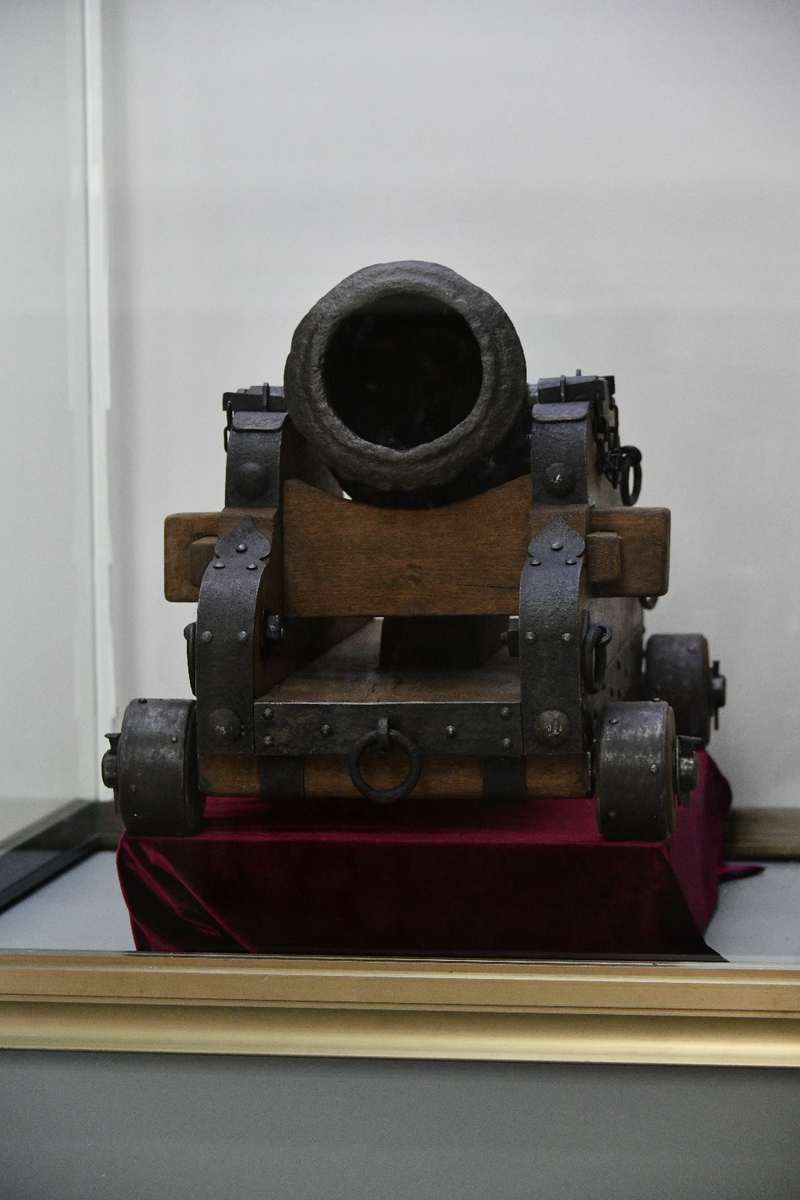
The cannon from Grinăuți-Moldova
 Fire artillery in Romanian space is attested from the first half of the 15th century. The oldest pieces of artillery are the bronze and iron bombards discovered in the fortresses of Giurgiu, Severin, Bârlad and Orheiul Vechi.
Fire artillery in Romanian space is attested from the first half of the 15th century. The oldest pieces of artillery are the bronze and iron bombards discovered in the fortresses of Giurgiu, Severin, Bârlad and Orheiul Vechi. The exposed cannon was discovered in the village of Grinăuți-Moldova, Ocnița district, it dates from the second half of the 15th century. From a typological point of view, in the central-eastern European space, the cannon from Grinăuți-Moldova is a unique piece. It is a short-barreled mortar-type artillery piece that fits perfectly into the line of bombards in Europe used in the second half of the 15th century - the beginning of the 16th century. The cannon was used to launch projectiles (bullets) at the enemy behind fortifications or natural obstacles. The projectiles were loaded through the mouth of the barrel. The firing angle was over 45 degrees, and the trajectory of the projectile was curved with a range of up to 300-400 m. In Europe, these cannons were called mortars, and in Romanian space they were designated by the word piua, thanks to the shape of this object. The cannon from Grinăuți-Moldova was discovered by chance in the "Red Bank" location, located 15 km southwest of the Lipnicu plain where Lord Stefan the Great defeated the Tatars in 1470. According to a legend from the village of Grinăuți-Moldova, in the "Red Bank" location, a military confrontation between Moldovans and Tatars would have taken place prior to the battle of Lipnic. The cannon from Grinăuți-Moldova is made of cast iron by the casting method. The barrel is provided with a single hole in the front, the opposite side being blocked by the flat bottom with flared edge. The inside of the pipe is a relatively wide channel that narrows slightly towards the bottom. Loading with powder and cannonballs was done through the mouth of the cannon. A hole is provided near the base for the wick to ignite and detonate the dust inside the cannon. The surface of the cannon is embossed. The edge of the mouth is thickened, slightly curved. Two cylindrical supports with a diameter of 3.5 cm are provided in the central part of the body of the cannon in the axis, which served as handles for the installation and handling of the cannon on a wooden frame. The length of the cannon is 30.0 cm, the maximum diameter of the body - 17.8 cm, the outside diameter of the mouth - 19.4 cm, the diameter of the body in the middle - 13.5 cm, the outside diameter of the base - 17.0 cm, the caliber of the cannon (mouth diameter) is 12.8 cm, the length of the inner chamber of the cannon - 27.4 cm, the weight of the cannon - 18,730 kg. The cannon from Grinăuți-Moldova entered the custody of the National Museum of History of Moldova through the care of local history teacher Vlad Lvovsky.
The conservation of the piece of cultural heritage was carried out by Valeriu Bubulici, and the reconstruction of the atmosphere by the restorer Mihail Culașco.
|
 31 August 1989 St., 121 A, MD 2012, Chisinau, Republic of Moldova
31 August 1989 St., 121 A, MD 2012, Chisinau, Republic of Moldova